Using gas sensors and an Arduino, you can build different kind of applications.
Examples of gas sensors:
- carbon dioxide (CO2) : MG-811
- carbon monoxide (CO): MQ-9
- total volatile organic compounds (TVOCs): CCS811
- equivalent carbon dioxide (eCO2): CCS811
- metal oxide (MOX): CCS811
- ammonia: MQ-137
- air quality: MQ-135
Example applications:
- Using a VOC and an ammonia sensor, you can build a “food sniffer”: more than 100 different volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can be detected in decomposing beef, pork, poultry and fish.
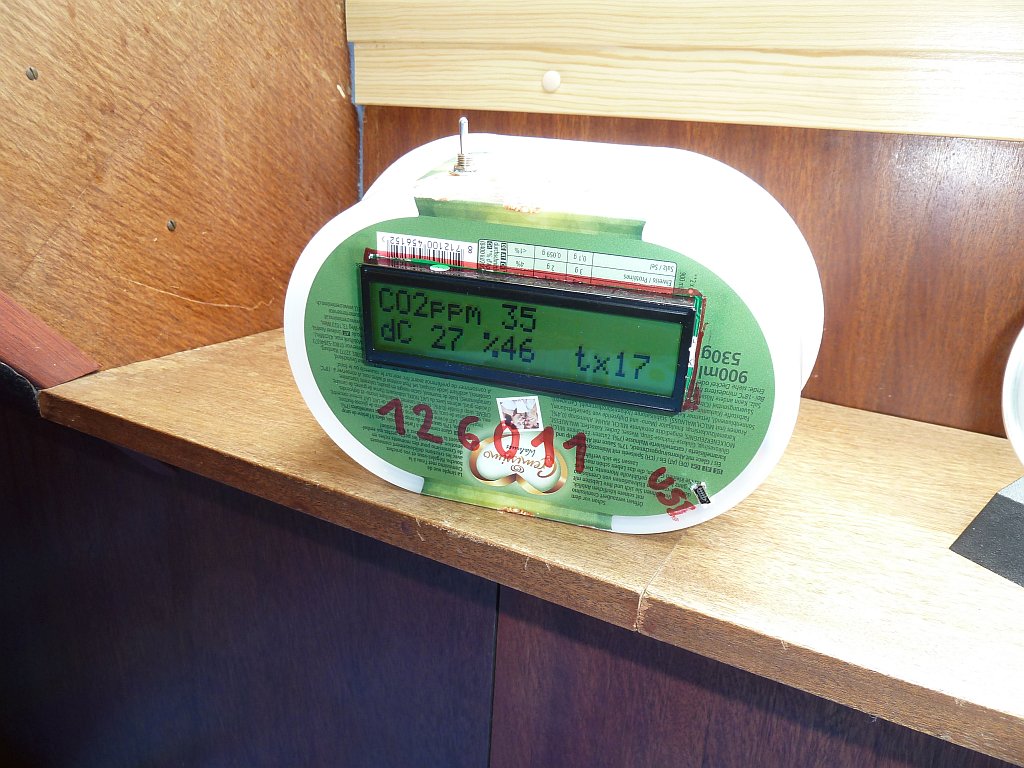
- Internet broadcasting weather station (CO2, temperature, humidity) made with Arduino
Live data:
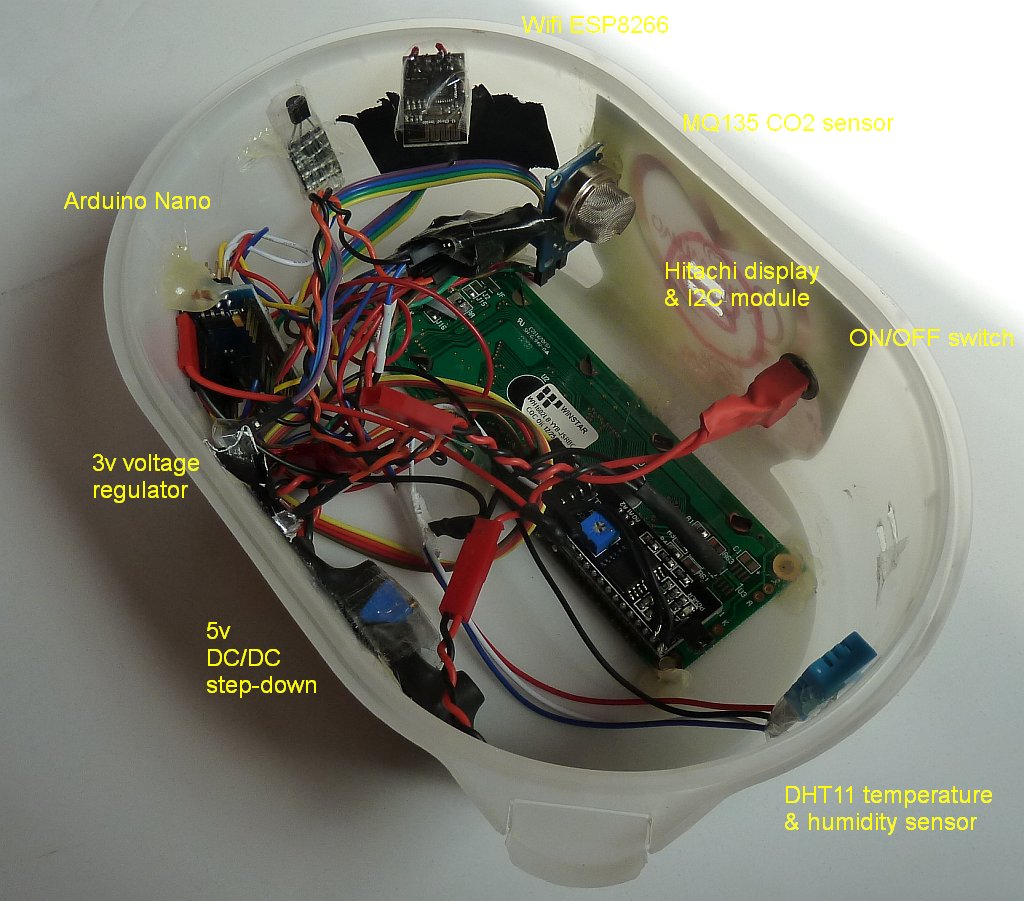
1. Data shown on display / Internet broadcast:
- CO2 (ppm)
- Temperature (°C)
- Humidity (%)
2. ThingSpeak Channel: https://thingspeak.com/channels/126011
4. Calibration of MQ135 sensor for CO2
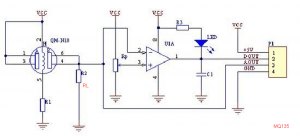
4.1. Measure RLOAD (kOhm) on your sensor PCB and adjust ‘RLOAD’ in MQ135.h
4.2. Find out the current atmospheric CO2: https://www.co2.earth/ and adjust ‘ATMOCO2‘ in MQ135.h
4.3. Let the sensor heat-up for 24 hours, leaving it in open air, then look for the ‘RZERO‘ output at Arduino start via Arduino IDE serial console (CTRL+SHIFT+M) and adjust ‘RZERO’ in MQ135.h
5. Ventilation
Ensure there’s enough ventilation, otherwise your case will heat-up, and measurements will be wrong.


Hi there, I read you topic, and can you please answer on this questions:
1. how to measure RLOAD (in KOhm) on sensor PCB?
2. how to find RZERO?
thanks
regards
Hello Roberto,
1. You can measure RLOAD using an ordinary Ohm-multimeter. I have added the sensor PCB schematics above and shown in it where to measure RL.
2. Let the sensor heat-up for 24 hours, leaving it in open air, then look for the ‘RZERO‘ output at Arduino start via Arduino IDE serial console (CTRL+SHIFT+M) and adjust ‘RZERO’ in MQ135.h
Regards,
Alexander
Nice project but i have one question..
Why you use MG-811 as co2 sensor instead of cheep mq135 sensor..??
(you don’t use it because they are also sensitive to other gases is it true..?? )