About: This is a Javascript online simulation of cascaded position and speed motor control for an FOC controlled motor. Use sliders to set params.
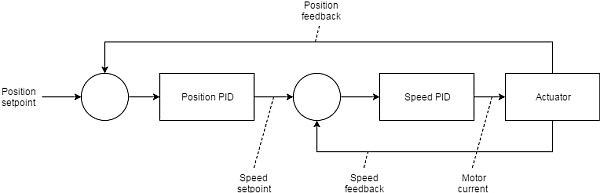
Position loop: pos_error = pos_setpoint - pos_feedback pos_integral += pos_error * pos_integrator_gain pos_differential = delta(pos_error) * pos_differential_gain vel_cmd = pos_error * pos_gain + pos_integral + pos_differential
Velocity loop: vel_error = vel_cmd - vel_feedback vel_integral += vel_error * vel_integrator_gain vel_differential = delta(vel_error) * vel_differential_gain current_cmd = vel_error * vel_gain + vel_integral + vel_differential
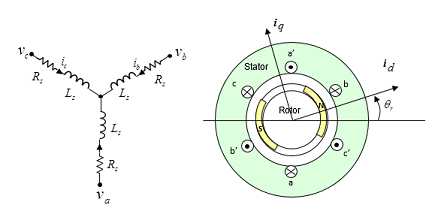
Motor model: Kt = 0.2 // Torque constant [Nm/A] Kv = 0.2 // Motor velocity constant or back EMF constant [V/(rad/s)] R = 2.5 // Phase Resistance [Ohm] L = 2.5e-3 // Phase Inductance [H] J = 1e-3 // Rotor Inertia [kg·m^2] B = 1.0e-4 // Rotor Friction [Nm/(rad/s)] tm = 62.5e-3 // mechanical time constant tm = R·J/(Kt·Kv) [s] te = 1e-3 // electrical time constant te = L/R [s] Motor equations: v = R·i + L·di/dt + ve ve = Kv·ω Te = Kt·i Te = TL + B·ω + JL·dω/dt; where: v - voltage [V] i - current [A] ve - back electromotive force [V] ω - angular velocity [rad/s] TL - Load torque [Nm] JL - Load inertia + Rotor inertia [kg·m^2]
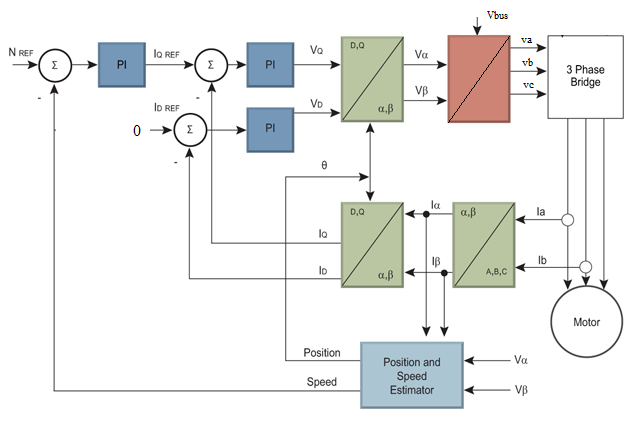
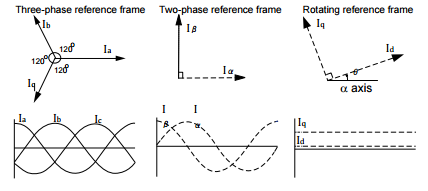
Clarke transformation into orthogonal stacionary reference frame: iα = ia iβ = 1/√3·(ia + 2ib); Park transformation into rotating reference frame id = iα·cos(θ) + iβ·sin(θ) iq = -iα·sin(θ) + iβ·cos(θ) where: θ - rotation angle PID iq_ref = -PID(rpm_ref-rpm)*Tmax/Kt // Kp = 5, Ki = 1e-5, Kd = 1000; Vq = PID(iq_ref-iq); // Kp = 0.5, Ki=0.01, Kd = 0 Vd = PID(id_ref-id); // Kp = 0.5, Ki=0.01, Kd = 0 Inverse Park transformation: Vα = Vd·cos(θ) - Vq·sin(θ) Vβ = Vd·sin(θ) + Vq·cos(θ) Inverse Clarke transformation va = Vα vb = -sin(30°)*Vα + cos(30°)*Vβ vc = -sin(30°)*Vα - cos(30°)*Vβ Voltage offset and amplify vn = (va+vb+vc)/3; va = (va-vn)*Vbus vb = (vn-vn)*Vbus vc = (vn-vn)*Vbus